Diabetes & Technology - CGMS & Insulin Pumps
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) is a medical technology used primarily by people with diabetes to continuously track blood glucose (sugar) levels throughout the day and night. A CGM system consists of a sensor, transmitter, and monitoring device (or smartphone app).
The sensor is a small device inserted under the skin (usually on the abdomen or arm) that measures glucose levels in the interstitial fluid (the fluid between cells).
The transmitter sends data from the sensor to a receiver or smartphone. The receiver displays the real-time glucose levels, trends, and alerts.
CGMs provide updates every 1–5 minutes, giving detailed insight into glucose trends, not just static readings like traditional finger-prick tests.
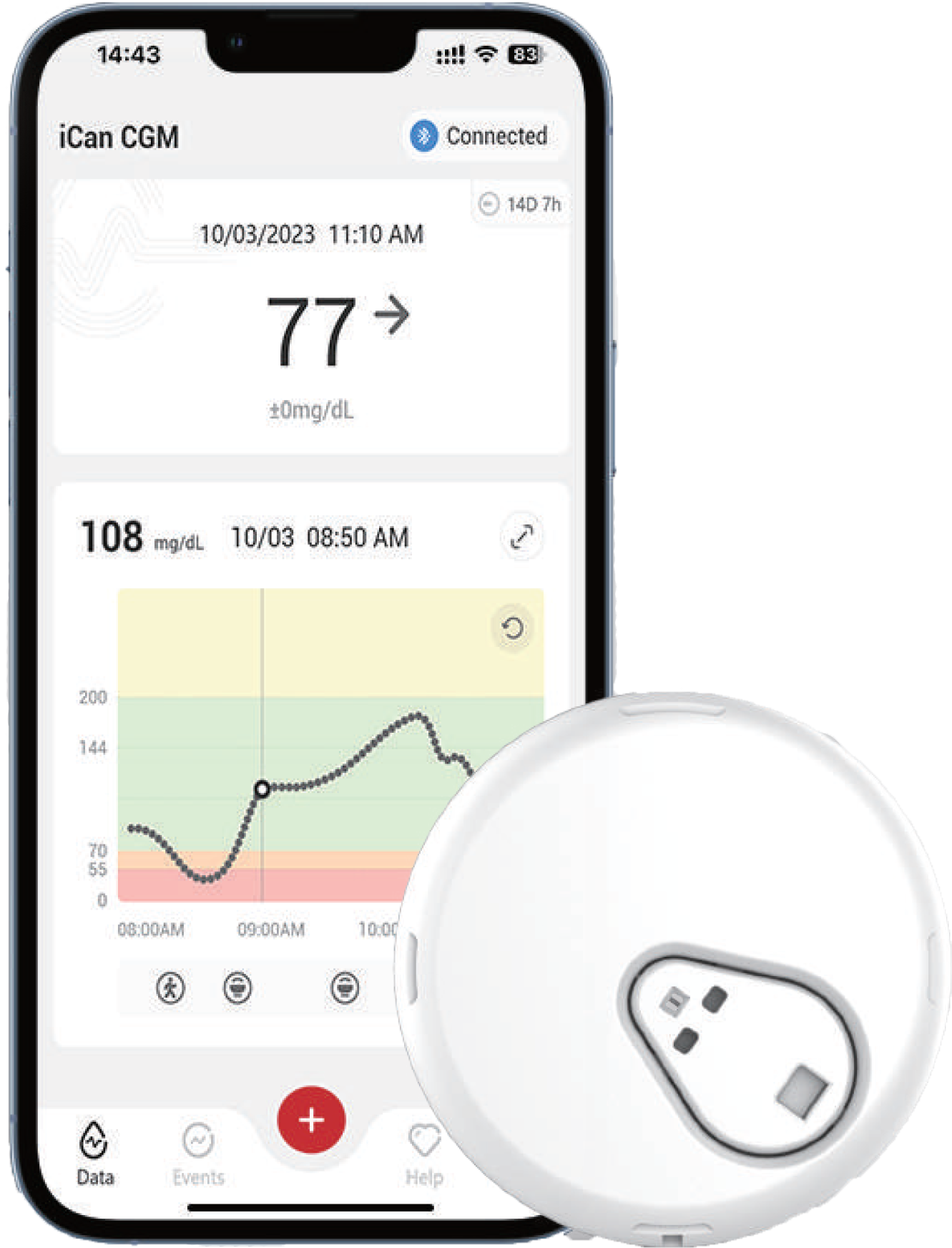
- Easy use App
- Reach App connects you with partners
- Customizable Glucose Alerts
- Bluetooth Connectivity
- IP28 Water Resistance
- No Calibration
- No Scanning
- No Finger pricks
Real Life Accuracy
sensor, transmitter and mobile application
reported convenient sensor attachment
reported comfortable insertion
reliable true alert rate
reported user APP convenience
- Real-time connectivity
- 15-day wear life
- Overall MARD 8.71%
- Monitors every 3 minutes

Importance of CGM

Improved Glucose Control
CGMs provide real-time glucose readings, helping individuals make immediate decisions about insulin, food, and exercise. By identifying glucose trends (rising or falling), users can prevent hypo- and hyperglycemia more effectively.
Reduction in Hypoglycemic Events
CGMs can issue alerts and alarms when glucose levels drop too low (hypoglycemia), especially useful at night when symptoms might go unnoticed.
Better Diabetes Management
CGMs help track how food, physical activity, medications, and stress affect glucose levels, leading to more informed and personalized diabetes management. They assist healthcare providers in adjusting treatment plans based on actual glucose patterns.
Improved HbA1c and Time-in-Range (TIR)
Regular CGM use has been shown to reduce HbA1c (a key marker of long-term blood glucose control) and increase time spent in target glucose range.

Convenience and Reduced Fingersticks
Many CGMs reduce or eliminate the need for frequent finger-prick testing. Some newer CGM models are factory-calibrated, requiring no fingerstick calibration at all.

Empowerment and Quality of Life
CGMs empower users with greater control and confidence over their diabetes. Parents of children with diabetes and caregivers of elderly patients can remotely monitor glucose levels, increasing safety and peace of mind.
An insulin pump is a small device that delivers insulin continuously (basal) or quickly (bolus) in response to carbohydrate intake. You can also correct a high blood glucose level by entering the amount of blood glucose or grams of carbohydrate to be eaten into the insulin pump. There's a variety of insulin pumps on the market, offering options to meet individual needs.
It’s important to begin with realistic expectations about what an insulin pump can and cannot do.
A pump can help improve blood glucose control, but it is essential to continue checking glucose levels using a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) or a glucose meter.
While the insulin pump continuously delivers insulin, it’s not a cure for diabetes. The goal is to manage your blood glucose levels more effectively while avoiding wide fluctuations and preventing severe hypoglycemia (low blood glucose).
How Insulin Pumps work
The information in the insulin pump is programmed to meet the individual's specific needs. Insulin is infused into fatty tissue through a small plastic tube, called a cannula, that's attached to a reservoir in the pump. The cannula is inserted under the skin by a needle, which is referred to as an infusion set. It's changed every two to three days to prevent infection. Only rapid-acting insulin is used in a pump. Since the pump continuously delivers insulin, there's no need for long-acting insulin.
Benefits of using an Insulin Pump
Studies indicate that an insulin pump can improve diabetes control and reduce the risk of hypoglycemia. Many individuals find they have greater flexibility with meals and exercise timing when using an insulin pump.
